Acquire AGIX Linux Support For Kubernetes & Docker
The AGIX Linux team of technicians has plenty of experience in deploying Docker containers and has written plenty of Kubernetes articles in the AGIX Linux technical block which is freely available to anyone interested in DIY computing.
Kubernetes & Docker Case Study
More systems are being distributed by Docker containers (images) in recent times due to the reliability and consistency of such a distribution method. AGIX Linux clients often request new systems which can easily and quickly be deployed using Docker.
The time saved by using Docker compared with traditional distribution and deployment methods is considerable, and the money savings is significant.
See Our Blogs on Kubernetes & Docker
Docker 101 – Get your head around Docker
All HowTo's
Kubernetes & Docker
Ubuntu, Mint & Debian Linux
Web Servers
In this article we’re going to walk through installing Docker on Ubuntu, starting a few Docker containers, and then running those containers behind a reverse proxy. When we’re done, you’ll have a load balance terminating SSL (TLS) connections with multiple Docker containers running the workload. This is how it will
Read More
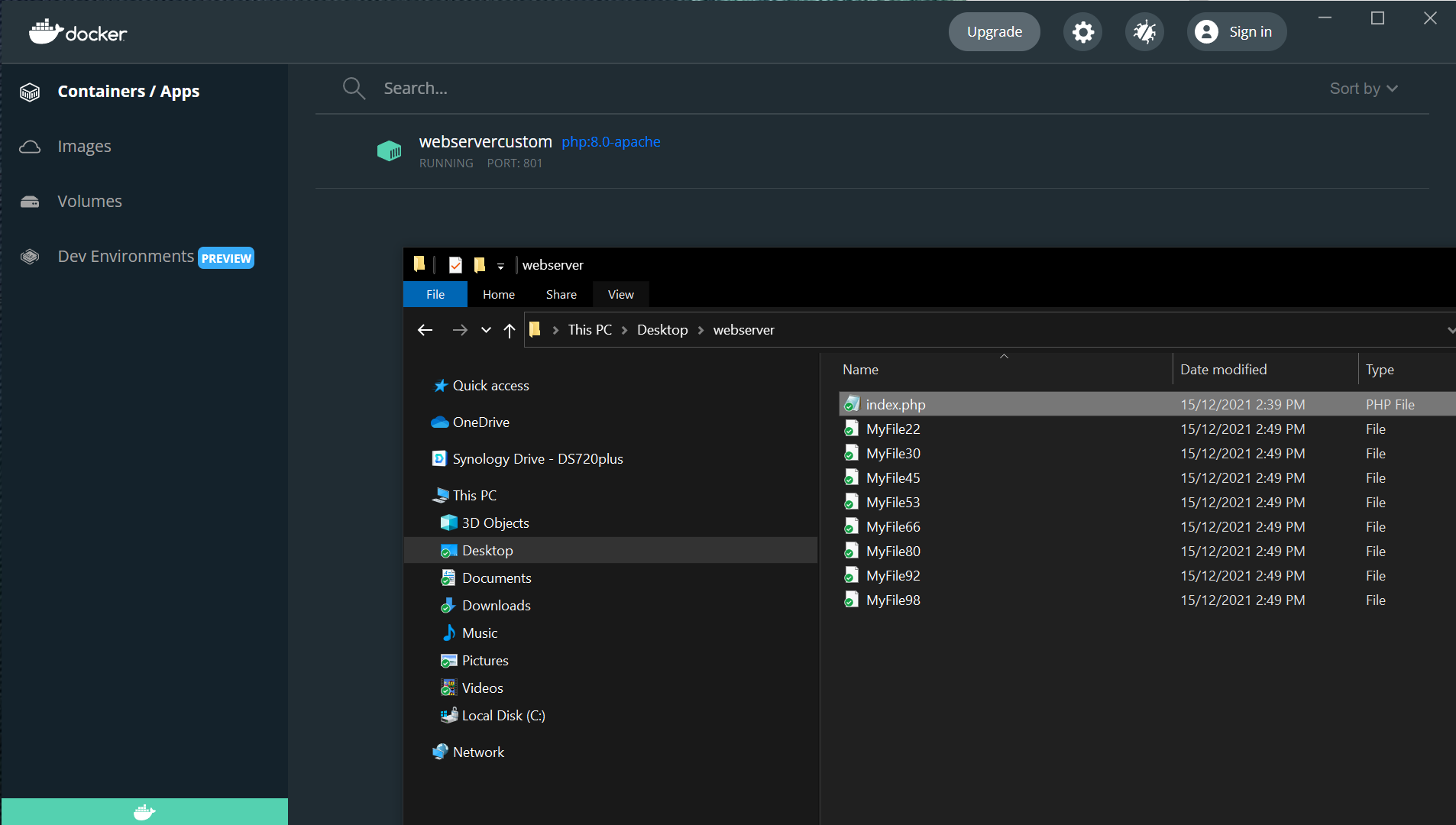
Docker for Windows – Install, run and launch a Web Server in Docker
Kubernetes & Docker
Web Servers
Windows
This article shows how to install Docker for Windows 10 (and probably 11), and then start a web server in a Docker container. Install Docker Visit “https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop” and download Docker installer. Start the installation process (you’ll need local admin privileges). During the installation process, the wizard will ask if you
Read More
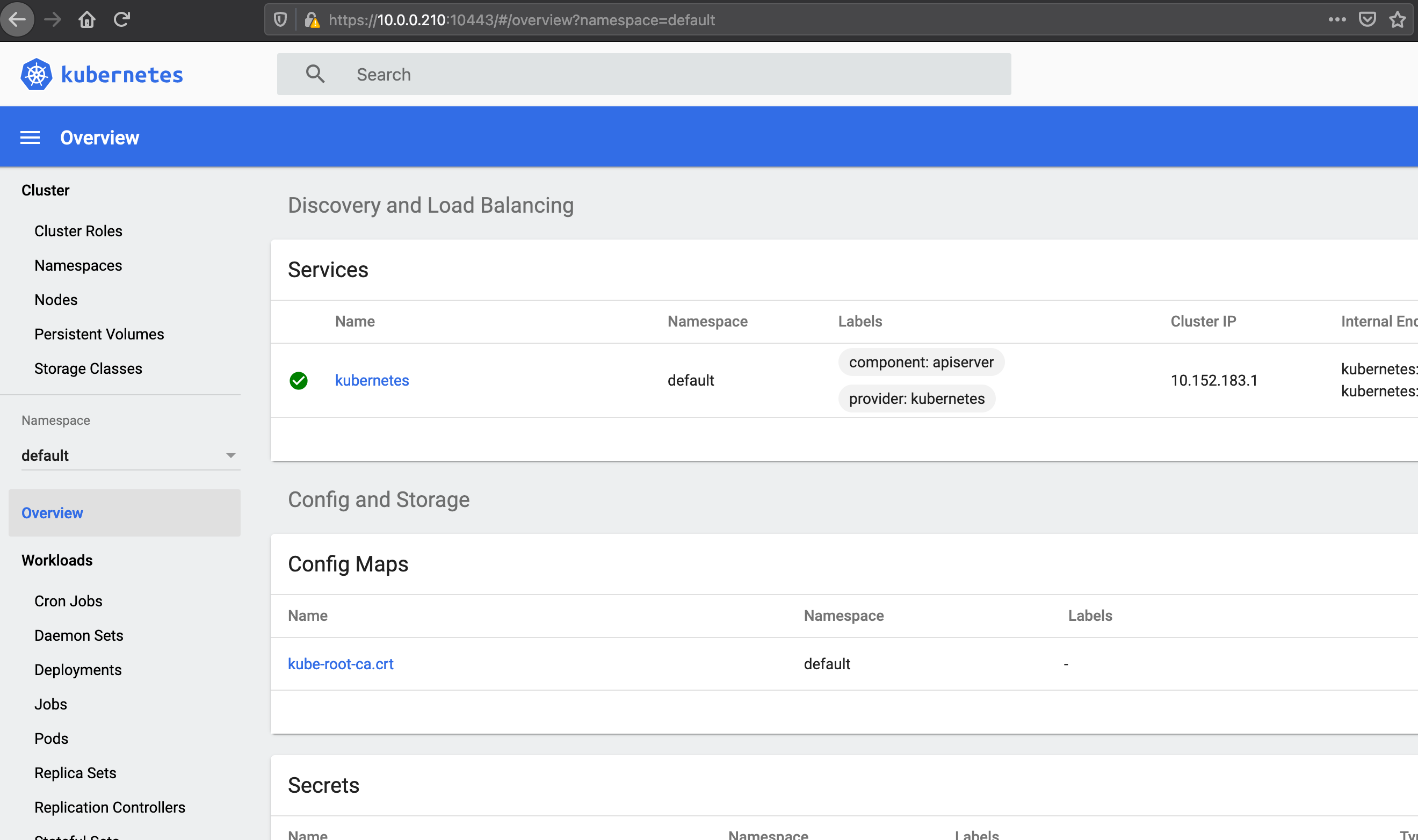
Kubernetes (MicroK8s) Part 4 – Microk8s in High Availability
All HowTo's
Kubernetes & Docker
The good news is that Microk8s can now be deployed in a multi-node architecture. And it’s simple to do. This video “https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dNT5uEeJBSw” is a nice demonstration. It uses a floating IP between the cluster nodes that removes the need to use a load balancer in front of your cluster. Start
Read More

Kubernetes (MicroK8s) Part 3 – Exposing Applications on Ubuntu 20.04
All HowTo's
Kubernetes & Docker
Linux
Ubuntu, Mint & Debian Linux
This article continues from Part 2 – Replica Sets and Scaling. Our objective in this article is to get an application exposed to the wider network on an IP address of the host and a port of our choice. The IP address will be “10.0.0.210” and our port of choice
Read More

Kubernetes (MicroK8s) Part 2 – Replica Sets and Scaling on Ubuntu 20.04
All HowTo's
Kubernetes & Docker
Linux
Ubuntu, Mint & Debian Linux
Web Servers
This article continues from Part 1 – Installation and configuration. We can create a replica set (replicateset) or “rs” for short, so we can scale an application to meet demand. Create a file on the Kubernetes host called “my-rep-set.yaml” and populate it with the following: Tip: This is just an
Read More

Kubernetes (MicroK8s) Part 1 – Installation on Ubuntu 20.04
All HowTo's
Kubernetes & Docker
Linux
Ubuntu, Mint & Debian Linux
Web Servers
This article walks you through the process of installing the minimal Kubernetes environment on Ubuntu 20.04. Kubernetes comes in two forms; a single node cluster and a multi-node cluster. In this walk through, we’ll be using the single node cluster called MicroK8s. I suggest starting with a Ubuntu 20.04 server
Read More
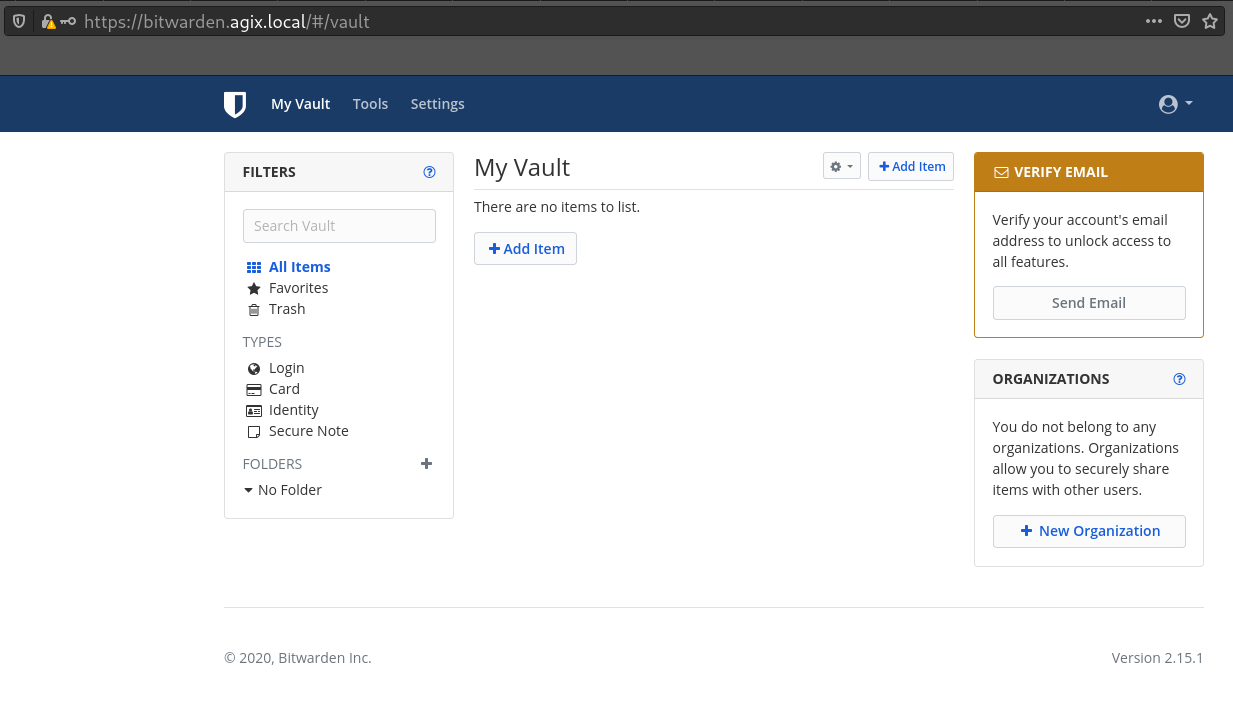
Installing Bitwarden in Docker on Fedora
All HowTo's
Cyber-Security
Kubernetes & Docker
Linux
Redhat, Fedora and CentOS Linux
Ubuntu, Mint & Debian Linux
This article is quick walk-through explaining how to install Bitwarden on Fedora 32 but should work on CentOS 7 and 8 as well as RHEL. Install the docker packages: yum install docker docker-compose systemctl enable docker systemctl restart docker Download the Bitwarden scripts: curl -Lso bitwarden.sh https://go.btwrdn.co/bw-sh chmod +x bitwarden.sh
Read More
Install OpenShift Origin on CentOS 6.4
All HowTo's
Kubernetes & Docker
Linux
Redhat, Fedora and CentOS Linux
This article describes how to install OpenShift Origin (the community version) on a Redhat or CentOS 6.4 server. We’re doing this as a test on an AWS EC2 CentOS 6.4 (With Updates) and a machine type of “m3.medium”. Do this on a fresh system, not one that has real previous
Read More
Need Help?
Click Here

